
The textile and apparel inspection procedure can ensure that fabric width, fabric length and fabric appearance comply with the relevant standards and regulations during the production process.
The purpose is of textile testing to assess the quality of the fabric, to analyze the structure of the fabric, to determine the fabric, to identify whether it meets the required standards.
After all, for today’s article, let’s move on to the textile inspection procedure and read the article in detail!!

Photo by Héctor J. Rivas on Unsplash
Fabrics: cotton, hemp, wool (sheep, rabbit), leather, silk, polyester, viscose, spandex, nylon, CVC, etc.
Various structural fabrics: woven (plain, twill, satin), knitting (weft, cotton, warp knitting), velvet, corduroy, flannel, lace, coated fabric, etc.
Garments: trousers, skirts, sweaters, t-shirts, cotton-padded clothes, down jackets, socks, children's clothes, etc.
Home textiles: sheets, quilts, bedspreads, towels, mattresses, etc.
Decorative supplies: curtains, tablecloths, wall cloth, etc.
Other: non-woven fabrics, masks, ecological textiles, antibacterial, bacteriostatic materials.
Physical indicators: the appearance of the fabric quality inspection, specifications size, defects, color difference, weft, the strength of the fabric, grammage, color difference, color fastness, etc.
Chemical indicators: formaldehyde content, PH value, odor, whether it contains banned dyes (azo dyes that can crack aromatic amines), heavy metals, fluorescence, APEONPEOPFOS, other banned surfactants, etc.
Taking performance: the feel of touch, smoothness, fluffiness and softness of the fabric, etc.

Photo by Janko Ferlič on Unsplash
International Standards: ISO, IEC, GATT
Regional standards: CEN, CENEL, ASAC, PASC, ARSO
Chinese National Standard: GB/FZ
American National Standard: ASTM
American Association of Dyeing and Chemical Authors: AATCC
EU Standards: EN
Japanese Industrial Standards: JIS
Australian National Standards: AS
British National Standards: BS
French Standards: NF
German Standard: DIN
Korean Industrial Standard: KS

Photo by Tingey Injury Law Firm on Unsplash
What is GB 18401, well, simply put, GB 18401-2010 standardizes safety requirements and testing methods for all textile products manufactured or sold in China.
It’s derived from the textile and apparel standards of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Here we will get into the details, classes of textile products, as well as areas of focus and testing.
Class 1: Products for babies (up to 36 months of age), which includes products such as cloth diapers, underwear, gloves, socks, bibs, outerwear, hats, and bedding items.
Class 2: Products with direct skin contact including blouses, skirts, shorts, pyjamas, socks, brassieres, bed sheets, towels, and hats.
Class 3: Products without direct skin contact including some sweaters and overcoats, bed covers, curtains, filling material, textile wallpaper and padding cloth.
GB 18401 focuses on testing for formaldehyde content, pH value, colorfastness, odor, and azo dyes. Compliance levels depend on the class of textile:
Formaldehyde content (mg/kg) -- measured against standard GB/T 2912.1
Class 1: (Not to exceed) 20 mg/kg
Class 2: 75 mg/kg
Class 3: 300 mg/kg
pH value -- measured against standard GB/T 7573
Class 1: 4.0 - 7.5
Class 2: 4.0 - 8.5
Class 3: 4.0 - 9.0
Colorfastness -- with tolerances based on the colorfastness scale (5 -- no fading, 1 -- extreme fading)
Water (GB/T 5713 change of color; staining) -- Class 1 (higher than 3-4); Class 2 and 3 (higher than 3)
Acid perspiration (GB/T 3922 change of color; staining) -- Class 1 (higher than 3-4); Class 2 and 3 (higher than 3)
Alkaline perspiration (GB/T 3922 change of color; staining) -- Class 1 (higher than 3-4); Class 2 and 3 (higher than 3)
Dry rubbing (GB/T 3920) -- Class 1 (higher than 4); Class 2 and 3 (higher than 3)
Saliva (GB/T 18886) change of color; staining) -- Class 1 (higher than 4)
Determination of odors -- measured against standard GB 18401, sec. 6.7
Azo dyes (mg/kg) -- measured against standard GB/T 17592.1. The Restricted list includes 24 decomposable aromatic amines believed to be both carcinogenic to humans and detrimental to the environment.
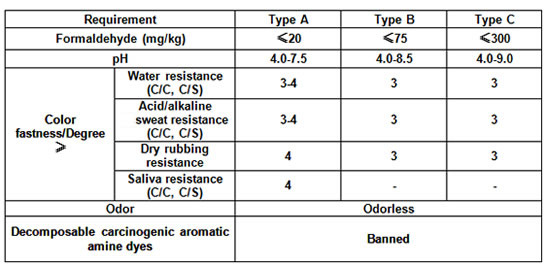
Source: Intertek
In textile industry, sampling is essential for produce export quality product. It depends on factors such as the form of material, amount of material available, nature of the test.
Test item | Sample(cm*cm) | Testing time |
Color fastness to washing | 30*30 | 2h |
Color fastness to rubbing | 50*50 | 1h |
Color fastness to perspiration | 30*30 | 6h |
Color fastness to water | 30*30 | 6h |
Color fastness to saliva | 30*30 | 6h |
Fibre composition | 50*50 | 1-2days |
Formaldehyde | 50*50 | 5h |
Ph | 50*50 | 3h |
Azo | 50*50 | 2days |
18401 Testing complete set | 100*145(1m) | 2days |
Unqualified Color Fastness:
A) Wash off the surface floating color (2 times in hot water above 60 degrees, then 2 times in cold water).
B) Add fixatives and soak for 2 hours.
C) Add the corresponding color fastness enhancer.
D)Send to a professional facility for treatment.
E) Prevent boiling in a pot, add laundry detergent (soap wash) and wash off the color after cooling, back and forth for several times for better results.
Unqualified Formaldehyde:
A) Place in a ventilated area for 1-2 days.
B) Use chemicals to wash off formaldehyde in a washing plant.
Unqualified PH:
If prone to be alkaline, add glacial acetic acid and soak.
If prone to be acidic, add a little water, or alkali for adjustment.
Unqualified Azo:
This problem cannot be handled perfectly now. Customized products are noramlly azo-free.

Photo by Lidya Nada on Unsplash
Textile color fastness test is a routine test item in the internal quality test of textiles. During its use, textiles will be exposed to various external effects such as light, washing, ironing, perspiration, friction and chemical agents.
Testing items mainly includes: washing color fastness, color fastness to dry cleaning, color fastness to rubbing, light fastness, color fastness to perspiration, color fastness to water stains, color fastness to saliva, pressing color fastness, color fastness to chlorine bleaching, color fastness to non-chlorine bleaching.

Photo by analuisa gamboa on Unsplash
The purpose of this testing is to obtain as much physical data on a textile sample as possible so that consumers can be assured of its contents and that it will be suitable for its intended purpose.
Physical Test mainly includes: GSM, linear density, diameter of fiber, ends per inch.

Photo by Bozhin Karaivanov on Unsplash
The trend of green consumerism has extended to textile and apparel products. Major European and U.S. textile product buyers have responded to this public awareness by viewing their textile products from an ecological standpoint, and are establishing relevant requirements. Eco-Testing mainly includes:
AP/APESs Quick Test
Banned Azo Colorants and Ozone Depleting Chemicals
Heavy Metal, Pesticide Residues, and Fungicides, such as Dimethyl fumarate
Formaldehyde Content
Eco-Textile Certification
GB 18401 Testing

Photo by National Cancer Institute on Unsplash
Textile testing is important in the sense that it allows companies, and corporations to deliver safe and good quality textiles for end customers.
Textile production is performed globally and sent to the market in cross countries as a trade opportunity. So, all harmful chemicals, impurities, or any other regulatory cracks are dealt with before sending the textile to customers.
Testing in itself matters a lot because the final product should be comfortable and safe to wear for end users.
After all, this is all about today’s article, it contain many professional words but would definitely be useful to your life. Anyway, what’s your ideas about textile and testing? Share your ideas with us!!